Honeybees vaccine
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) approved the first ever vaccine for honeybees at the beginning of January 2023, to protect them against American Foulbrood (AFB). The vaccine was developed by biotech co. Dalan Animal Health, an Athens, Georgia, USA-based vaccine platform that provides sustainable solutions for a safe food supply.
Dalan’s honeybee vaccine is the first prophylactic solution against American Foulbrood. American Foulbrood is a fatal bacterial disease caused by Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae (a spore-forming bacterium that is resistant to oxytetracycline antibiotic). It is considered the most infectious of honeybee brood diseases and globally the only effective method of eradication has been a combination of intense monitoring, high levels of hygiene followed by the burning of the infected colonies and equipment used in association with those infected colonies.
Some honeybee strains are partially tolerant to AFB – but it is not a solution
There is evidence of partial resistance or greater tolerance in higher hygiene prevalent honeybee strains such as the Russian Honeybee and the VSH (Varroa Sensitive Hygiene) honeybee. Higher hygienic behaviour in honeybees manifests as an ability to identify and remove infected bee larvae earlier from the colony and so before the infection has a chance to spread further.
However, AFB tolerance only conveys a partial solution and is relatively rare in commercial honeybee strains. One research paper by Spivak and Reuter from the University of Minnesota found that 39% of AFB tolerant bee colonies developed AFB clinical symptoms and of these 7 colonies, 5 recovered.
In contrast, 100% of non-hygienic colonies displayed AFB clinical symptoms and only one colony recovered. Diseased non-hygienic colonies produced significantly less honey.
Exhibit 1 – AFB infection cycle
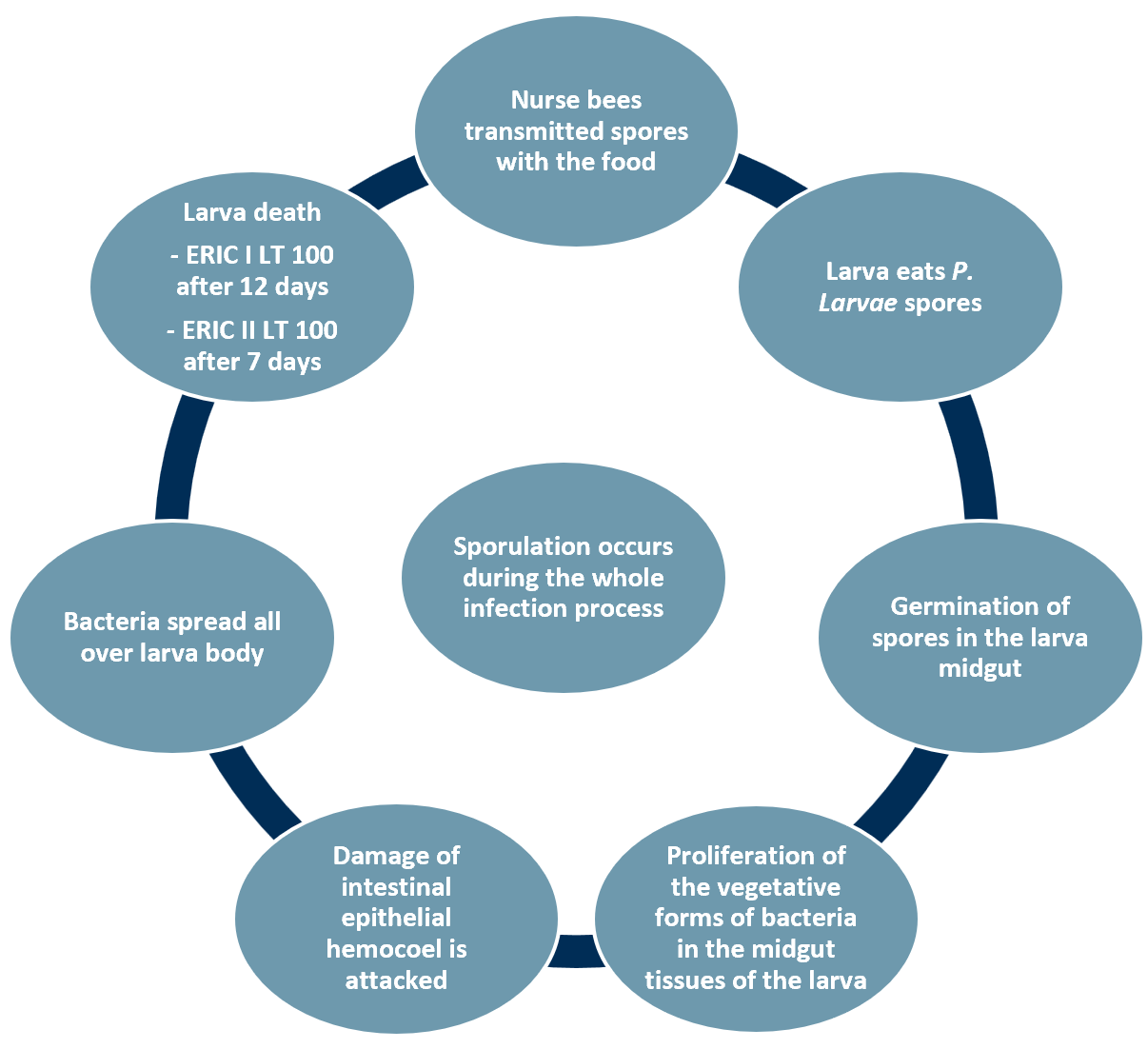 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Woodrow, 1942; Genersch et al., 2006; Yue et al., 2008.
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Woodrow, 1942; Genersch et al., 2006; Yue et al., 2008.
Antibiotics can be used to combat AFB – at cost and with attendant risks and complications
Antibiotics used with AFB infected colonies are usually introduced via feed mixtures or by spraying the colony. Antibiotics have to be applied by a vet and are often used only as a last resort, with some bee keepers showing a preference for improving nutrition to improve AFB tolerance in colonies.
The antibiotics tetracycline, oxytetracycline, lincomycin and macrolide antibiotic tylosin are used individually or in combination to treat AFB infected colonies with success.
However, there is already evidence of tetracycline resistance – this resistance can be passed on to other species or types of bacteria. Antibiotics can also kill useful bee ecosystem bacteria and there is evidence that lincomycin kills beneficial bee gut bacteria (which appears to be a parallel to the gut biome side-effect of antibiotic use in humans and other animals).
The Dalan vaccine implied opportunity
Exhibit 2 – Leading honeybee colony mortality reported in the field in Europe 2010
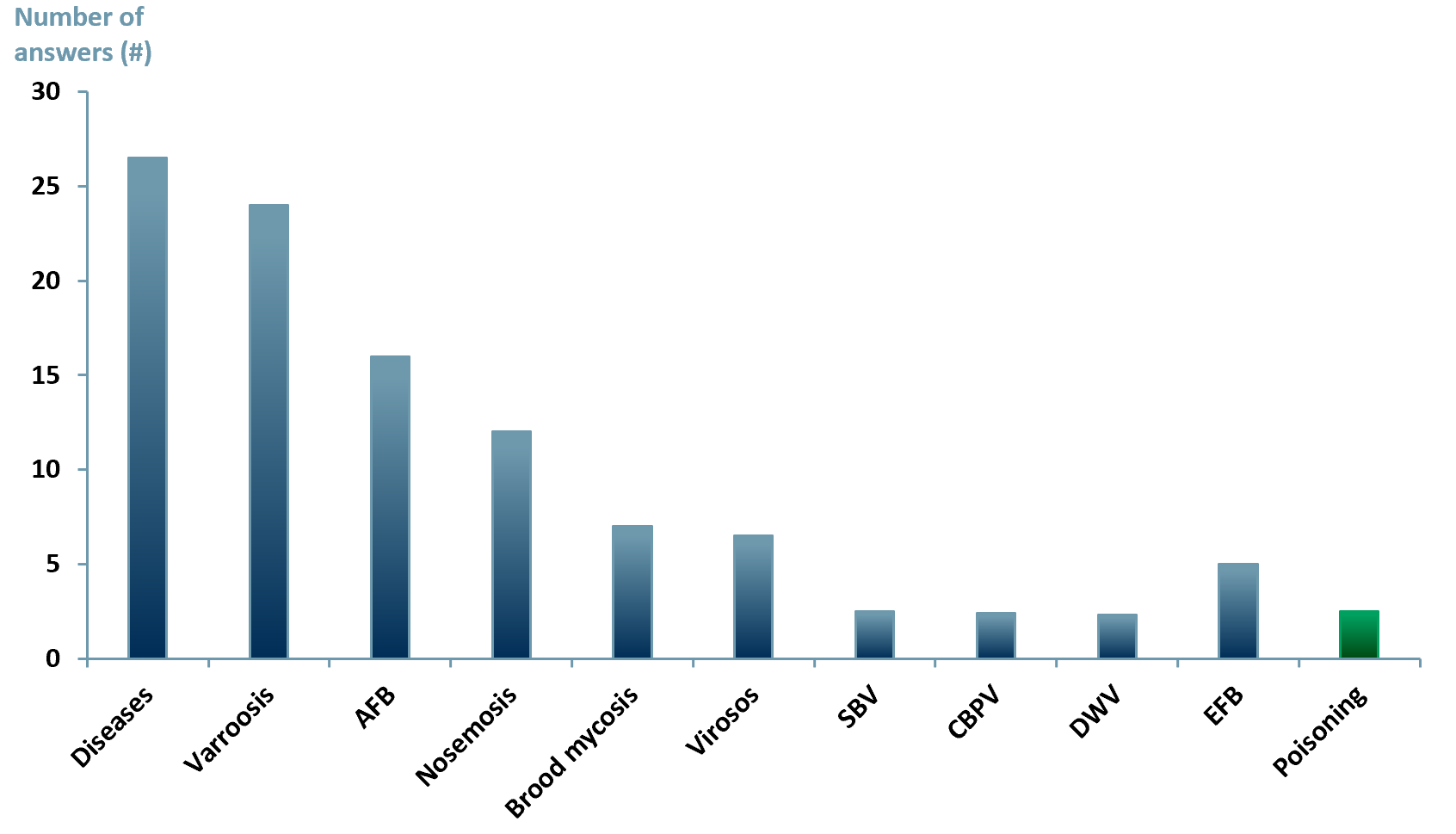 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, SBV: Sacbrood virus, CBPV: Chronic bee paralysis virus, DWV: Deformed wing virus, EFB: European foulbrood.
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, SBV: Sacbrood virus, CBPV: Chronic bee paralysis virus, DWV: Deformed wing virus, EFB: European foulbrood.
Exhibit 3 – Leading honeybee colony mortality reported by laboratories 2010
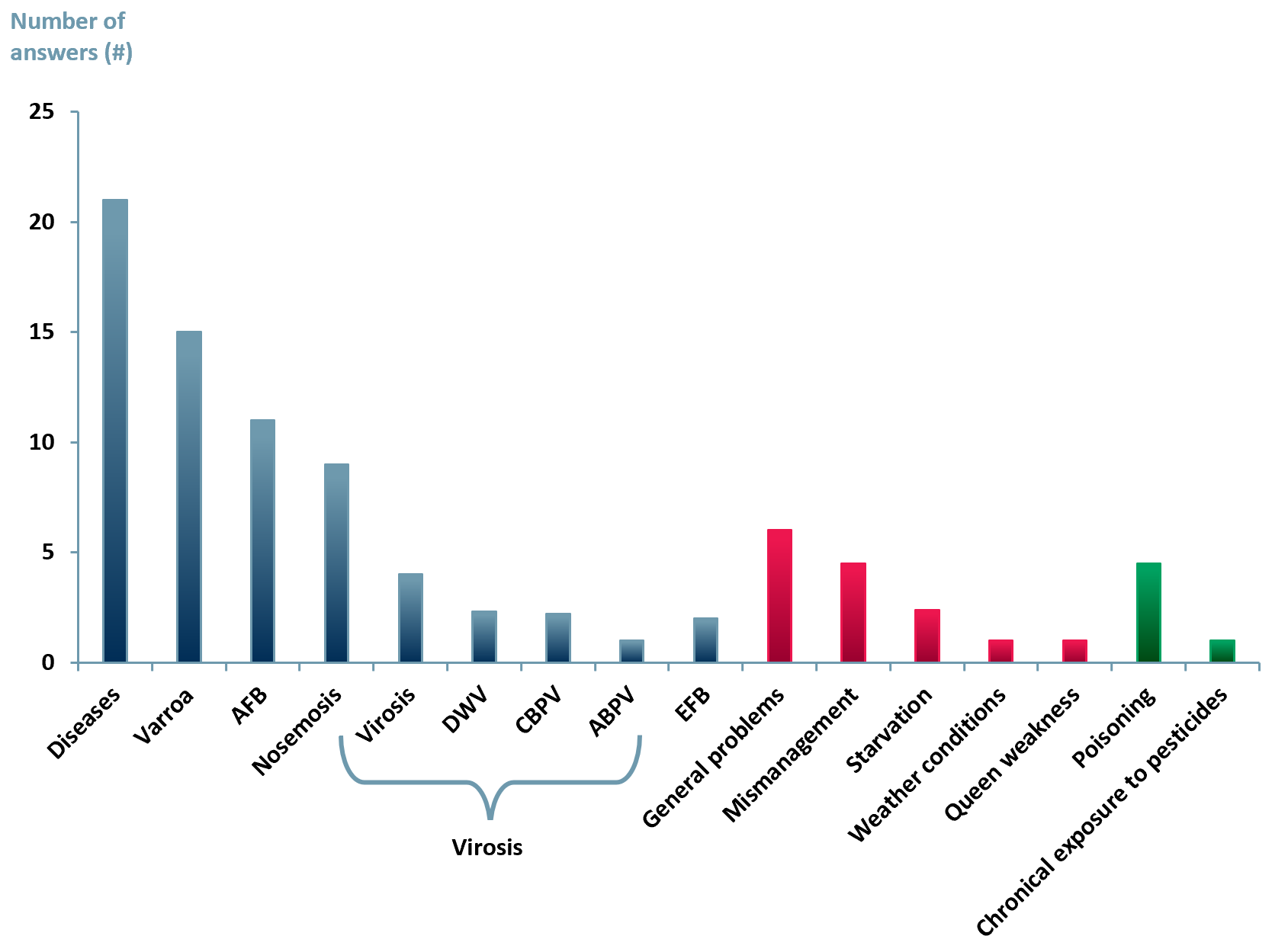 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, SBV: Sacbrood virus, CBPV: Chronic bee paralysis virus, DWV: Deformed wing virus, EFB: European foulbrood.
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, SBV: Sacbrood virus, CBPV: Chronic bee paralysis virus, DWV: Deformed wing virus, EFB: European foulbrood.
Exhibit 4 – Leading honeybee colony mortality reported by beekeepers 2010
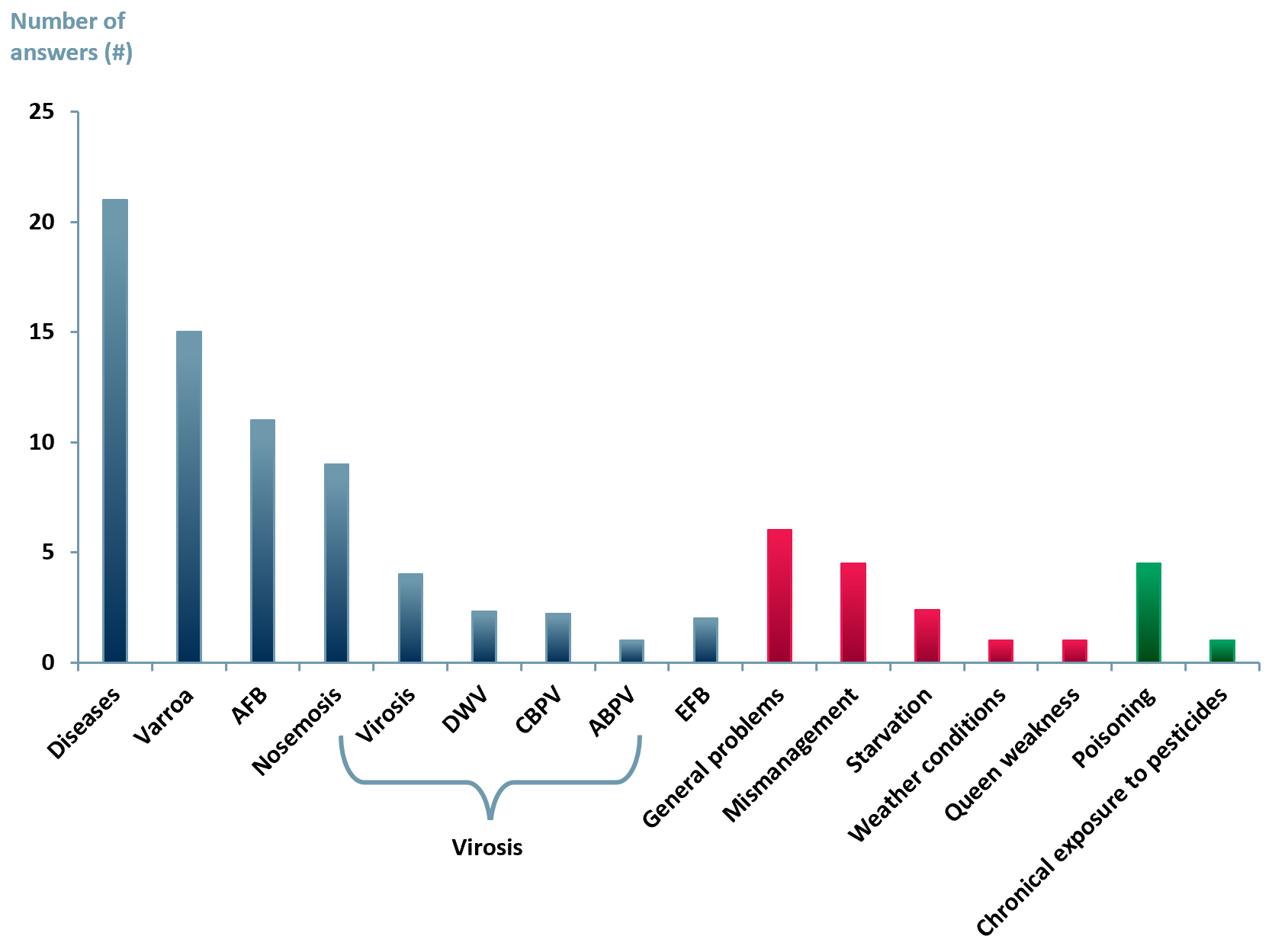 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, EFB: European foulbrood.
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Plos One Journal – Demographics of the European Agricultural Industry 13/11/2013. Notes: Diseases: non-specified diseases AFB: American foulbrood, EFB: European foulbrood.
How does the newly licensed Dalan developed vaccine work and how is it applied?
The vaccine is administered as follows:
• A dead version of Paenibacillus larvae and is incorporated into royal jelly (a honeybee secretion used in the nutrition of larvae and adult queens).
• Once ingested, the vaccine deposits itself in the queen bees ovaries, providing larvae immunity as they hatch.
Dr. Dalial Freitak from the University of Graz (Universität Graz) in Austria and other researchers, identified the specific protein in honeybees that prompts an immune response in their offspring. Their studies found that immunity could be cultivated in the bee population by a single queen.
Vaccine resistance
The vaccine approach is receiving praise because it is recognised as a preferential approach when compared to burning colonies and equipment and the use of antibiotics. Nevertheless, bacteria are also capable of becoming vaccine (as well as antibiotic) resistant. For example, in humans, vaccine resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae have been identified.
Honeybees are responsible for only 30-35% of crop pollination but this statistic belies their importance…
Though the estimated contribution of honeybees to crop, vegetable, fruit and nut yields in the global supply chain is estimated at only 30-35%, this is a highly significant overall contribution and their loss would result in a collapse in global food supply, which in turn would inevitably contribute to triggering famines and migration pushes, which tend to lead to human armed conflict. The decline of honeybee colonies and their survival rates is a forward indicator for the decline of all pollinators.
The advent of the Dalan vaccine is to be welcomed and applauded and is a significant investment sub-sector opportunity. However, we see vaccine solutions as buying time. The real solution is better ESG driven by investor choices, so the allocation of capital in a way that improves and incentivises companies (and governments) to implement conservation and management processes and protocols that reinvigorate and protect the natural environment.