AI expands gene therapy’s accessibility
Dyno Therapeutics published research on ‘AI in gene therapy’ on 11 Feb. The study shows that AI could transform gene therapy and increase accessibility.
- Gene therapy currently has limited applications as 50-70% of the population has an existing immunity to adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids, which are used in gene therapy.
- To overcome this, functional variants from a wider diversity of AAV capsids need to be identified that can evade the immune system.
- With the assistance of AI, Dyno was able to generate a record number of AAV capsids – 200k. 60% of these viral vectors were estimated as usable in engineering capsids for gene therapies.
- Research collaborators included Google research, Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the Harvard Medical School laboratory of George M. Church, Ph.D. (a Dyno scientific co-founder).
Artificial intelligence (AI) adoption in healthcare is increasing. AI and healthcare has converged over last ten years – advancements in machine learning processes have already enabled the development of breakthrough devices, such as robotic surgeons and doctors, and in turn treatments.
As ACF has argued previously, opportunities remain abundant for AI integration into healthcare. We continue to argue that the healthcare sector (pharma, biotech, services, care, telemedicine, devices, diagnostics) is only scratching the surface in terms of the value generation AI has to offer the sector.
AI in biotechnology
AI is starting to have an impact within the biotechnology sector, in the following ways:
Drug discovery – Non-AI new drug development on average takes approximately 12 years and US$ 1bn (Pfizer). According to market consensus, the use of AI can reduce this to two to four years. The covid vaccines took less than 12 months.AI also reduces development costs by streamlining and standardising data. AI is able to sort and cross-reference pharma company databases that hold thousands if not millions of compounds.
Personalised medicine – The Covid-19 pandemic has brought into acute focus what we already knew – no one patient is the same. Through AI, pharma companies are analysing individual patient data in order to provide ‘micro targeted’ treatment options.
Diagnostics – The healthcare industry is examining how to use AI to improve disease early detection. A study published in The Lancet Digital Health (a journal focused on digital technology and health) states that the level of detection accuracy of AI is 1% higher than that of a medical professional. This margin of efficacy will improve.
Gene therapy
Gene therapy works by introducing normal or healthy genes into cells that are missing or have defective genes. Research scientists aim to use genes on a broad basis as an alternative to drugs or surgeries in treating diseases.
Gene therapy involves the insertion of healthy genes into the patient’s cells to help in fighting different health conditions such as haemophilia, Parkinson’s, cancer and HIV.
While gene therapy may still be in the experimental phase, the US’s Federal Drug Administration (FDA) has approved 19 gene therapy products to date. These include Luxturna (for patients with biallelic RPE65 mutation-associated retinal dystrophy) and Kymriah (used in adult patients with large B-cell lymphoma).
As the efficacity of gene therapy increases, we will see more companies entering the market.
In exhibit 1 our peer group that focuses on the development and delivery of gene therapy products – Roche Holdings AG (ROG:SWX), Novartis AG (NOVN:SWX), Amgen Inc (Nasdaq:AMGN), Gilead Sciences (NasdaqGS:GILD) and Sarepta Therapeutics (NasdaqGS:SRPT).
Exhibit 1 – Peer group of companies operating in the gene therapy sector
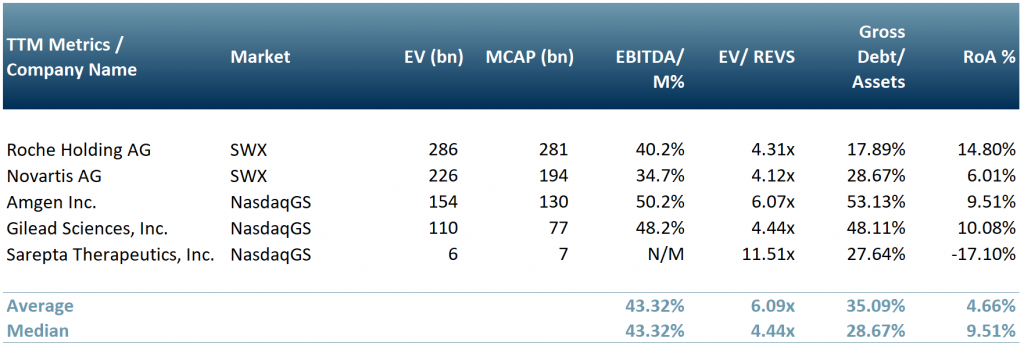
Source: ACF Equity Research Graphics
Globally, the gene therapy market is projected to reach US$ 35.67bn in 2027 up from US$ 3.61bn in 2019, exhibiting a CAGR of 33.6%. (Fortune Business Insight)
ACF forecasts a slower growth with a CAGR of 30% between 2020E to 2023E due to Covid-19 pandemic limitations where clinical trials have experienced significant delays. This is not to say that we are not bullish about gene therapy, rather we are realistic about the effects of covid on trial schedules.
Between 2024 to 2030 ACF forecasts that the growth rate in the gene therapy market will accelerate, touching 35% due to Covid-19 vaccine rollouts, improved capex budgets in R&D healthcare and the wider applicability of gene therapy as it expands into neurology and oncology. (See exhibit 2).
Note that we also infer that covid is not over because of the vaccine rollouts. The problem is that covid is in the population now and will continue to mutate. The vaccine producers may keep up but there will always be a lag and that will keep large sections of the public and governments cautious.
Nevertheless, we remain optimistic about the growth of the gene therapy market over the longer term, we infer that it will overtake the entire pharmacological in terms of total market in due course.
Exhibit 2 – Global gene therapy market size 2020E – 2030E
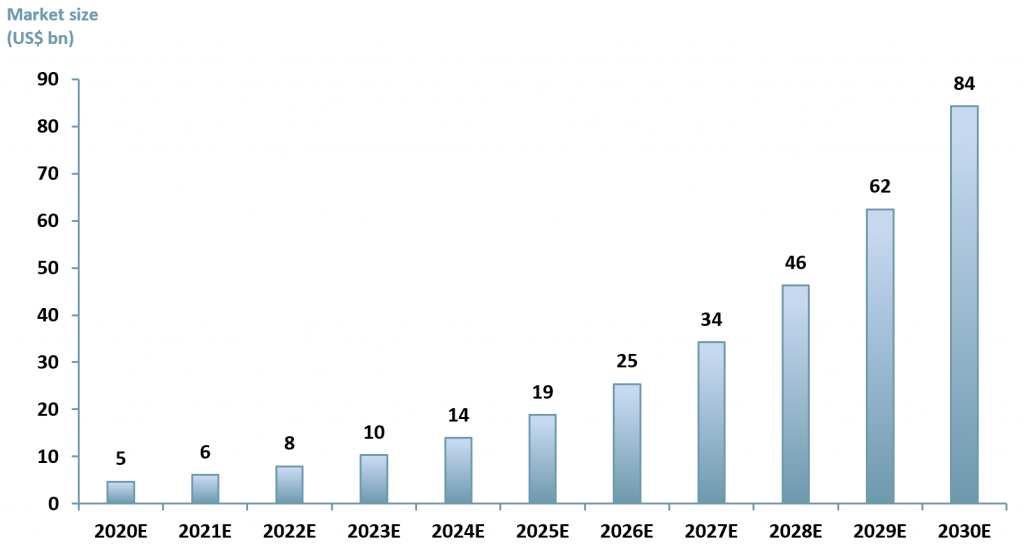 Sources: ACF Equity Research Estimates; Fortune Business Insights.
Sources: ACF Equity Research Estimates; Fortune Business Insights.
Author: Anda Onu – Anda is part of ACF’s Sales & Strategy team. See Anda’s profile here