Could solid-state batteries be the future?
Is solid-state battery technology just another hype? The markets are speculative as producing solid-state batteries to scale remains unpredictable.
Key Points:
- QuantumScape Corporation (NYSE:QS), backed by Volkswagen with a US$ 300m investment, jumped to a valuation of US$ 50bn in Dec 2020 after claiming to have made a breakthrough in solid state battery technology.
- Instead of using a liquid electrolyte (as in current lithium-ion batteries), solid state batteries use a solid electrolyte. In the case of QuantumScape they use an anode made from pure lithium.
- For years, the barrier to solid state batteries with a pure lithium anode (attractive because it has a high energy density) has been the formation of lithium dendrites (or whiskers). These grow on the pure lithium metal of the anode creating unwanted reactions between the electrolyte and lithium, causing battery failure.
- QuantumScape claims to have created a solid separator that can stop the damage caused by dendrites. If proved correct, this would be a significant leap in battery innovation.
- The company’s valuation has since fallen as doubts have grown over the validity of the data.
Solid-state vs. Lithium-ion batteries
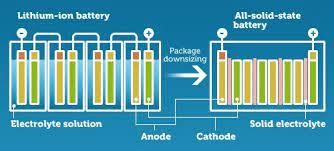
The main difference between the two types of batteries is that Lithium-ion uses a liquid electrolyte solution and Solid-state uses a solid electrolyte. The electrolyte is the battery’s conductive chemical, which facilitates the flow of the electron current (from the anode to the cathode).
Solid-state batteries can hold twice as much energy as Li-ions. This is because solid-state batteries only need thin separators (3-4 microns each) between the solid electrolyte whereas Li-ions require much larger separators (20-30 microns each). [1 micron (1μ) = 1/1000 millimetre]
Exhibit 1 – Solid-state vs. Lithium-ion battery
 Source: Android Authority
Source: Android Authority
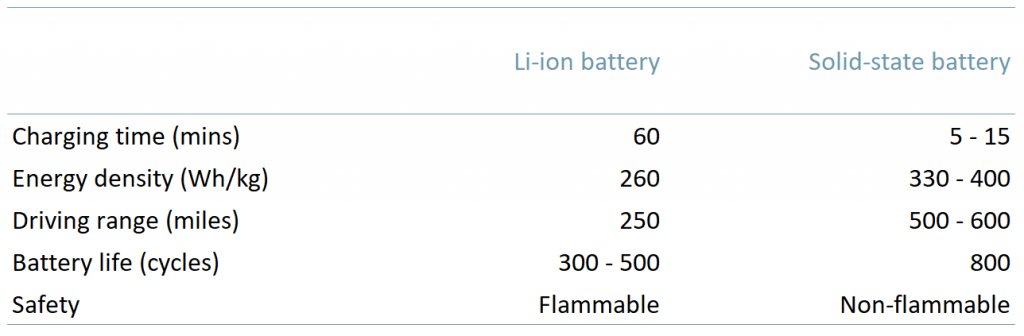
Exhibit 2 – Solid-state and Lithium-ion battery characteristics
 Source: ACF Equity Research Graphics
Source: ACF Equity Research Graphics
While the stats are a clear indication that solid-state batteries are a better alternative for EV vehicles, why is there such push-back from the markets?
Solid-state batteries: a nagging sentiment…
QunatumScape (QS) appears to be a pioneer (assuming data presented is verifiable) in this industry where many other companies have failed – QS suggested it has developed a ceramic material, no larger than a playing card, that allows batteries to charge to 80% in just 15 min.
QS was mentioned by former Nobel Prize in Chemistry winner Stanley Whittingham who said that he ‘had not seen data this good, such as that provided by QuantumScape, anywhere else’.
However, others in the markets are less optimistic. The main concern is producing these batteries to scale, where they can fit into an electric vehicle (EV). As with any potentially ground-breaking discovery, the practical mass market execution will take some time.
Momentum
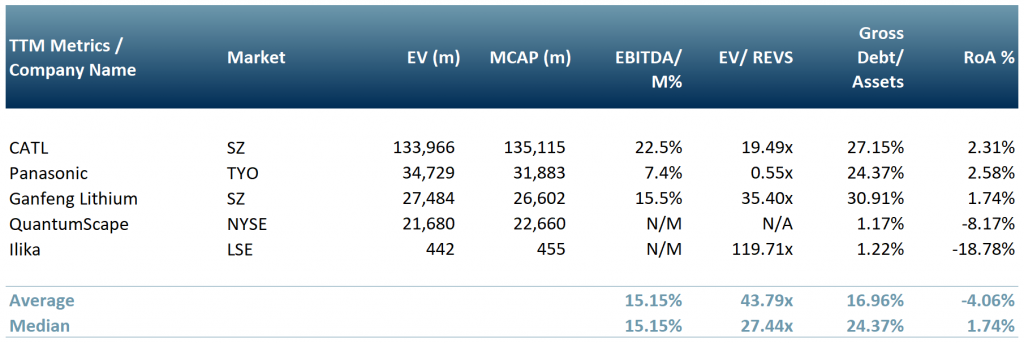
In Exhibit 2 below, we show a peer group of companies working in the solid-state battery industry – Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (300750:SZ), Panasonic Corporation (6752:TYO), Ganfeng Lithium Co., Ltd (002460:SZ), QuantumScape Corporation (NYSE:QS) and Ilika Plc (IKA:LSE).
Exhibit 3 – Peer group table of public companies engaged in the development of solid-state batteries
 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Yahoo Finance
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Yahoo Finance
Currently, the EV market is dominated by Tesla (NasdaqGS:TSLA) and ACF forecasts that by 2030E Tesla will win 20% market share, up from ~18% in YE20A. Tesla’s EVs use lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. However, the QuantumScape example suggests that the solid-state industry could be on the road to providing a commercially viable mass alternative to Li-ion technologies.
Solid-state battery powered buses have already been released by Dailmer AG (DAI.DE:XETRA) and NIO Limited (NYSE:NIO) alerted markets that it has plans for solid-state battery powered vehicles by 2023.
Other car manufacturers such as Ford Motor Company (NYSE:F) and Volkswagen AG (VOW.DE:XETRA) have shown interest by investing in separate solid-state battery companies (Solid Power and QuantumScape, respectively).
Exhibit 4 – Peer group table of EV auto manufacturers developing or planning to develop solid-state battery EVs
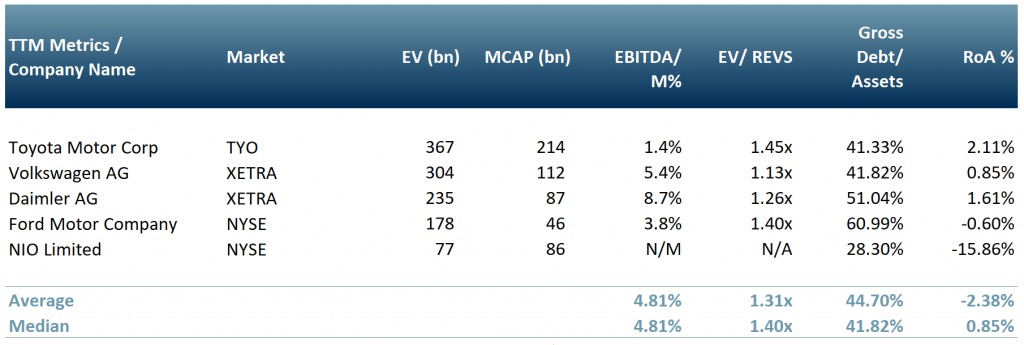 Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Yahoo Finance
Sources: ACF Equity Research Graphics; Yahoo Finance
Although promising, solid-state battery technology is still in its early stages in terms of mass production and it will take some time to create a battery that markets, manufacturers and consumers are confident is commercially viable. Panasonic believes the technology will be commercially available en-masse by 2030E and has the potential as a long-term future power source for EVs.
Covid has significantly concentrated the global focus on climate change and moved it up the consumer priority list. Developments in battery technology have (fortuitously) hit a market with open ears, and cash to invest – retail investors, SHNWI’s, FOs, institutional FMs/PMs – If solid-state batteries are indeed environmentally / sustainability / ESG friendly, the investment opportunities are…extensive.